What is Solid Waste ?
Solid waste refers to any discarded material that is in solid or semi-solid form. It includes a wide variety of items discarded by households, industries, agriculture, healthcare facilities, and commercial establishments. Solid waste can range from biodegradable materials to non-biodegradable items that persist in the environment.
Different Solid Waste Treatment Methods

What is Solid Waste Management ?
It refers to the systematic control of the generation, storage, collection, transfer, transport, processing, and disposal of solid wastes in a way that is environmentally and socially responsible.
Methods of Solid Waste Management
1. Landfilling: Waste is buried in designated areas (landfills). Properly managed to reduce contamination of groundwater and minimize gas emissions.
- Advantages: Simple and cost-effective.
- Disadvantages: Space requirements and potential environmental issues.
2. Incineration: Waste is burned at high temperatures to reduce its volume. Often used to generate energy in Waste-to-Energy (WTE) plants.
- Advantages: Reduces waste volume significantly and generates energy.
- Disadvantages: Expensive and emits greenhouse gases.
3. Recycling: Conversion of waste materials into reusable materials. Common materials: paper, plastics, metals, and glass.
- Advantages: Conserves resources and reduces landfill use.
- Disadvantages: Requires sorting and can be cost-intensive.
4. Composting: Organic waste is decomposed into nutrient-rich soil through biological processes. Commonly used for food scraps and garden waste.
- Advantages: Produces natural fertilizer and reduces organic waste.
- Disadvantages: Time-consuming and requires space.
5. Waste Minimization: Focuses on reducing the generation of waste through techniques like source reduction and reuse.
- Advantages: Most sustainable method
- Disadvantages: Requires significant behavioral and systemic changes.
➢ Challenges in Solid Waste Management
- – Lack of infrastructure and funding.
- – Insufficient public awareness and participation.
- – Environmental and health hazards due to improper disposal.
Hazardous waste management
Hazardous waste management is the process of handling, treating, and disposing of waste materials that can be dangerous to the environment, public health, and ecological systems. Hazardous waste can be solids, liquids, sludges, or contained gases. It’s often generated by manufacturing, chemical production, and other industrial activities.
➢ Types of Hazardous Waste
1. Chemical Waste: Includes acids, solvents, pesticides, and heavy metals.
2. Biological Waste: Infectious medical waste like used syringes and contaminated materials.
3. Radioactive Waste: Waste from nuclear plants, laboratories, and medical applications.
4. Industrial Waste: Toxic by-products from factories, refineries, and mining operations.
➢ Steps in Hazardous Waste Management

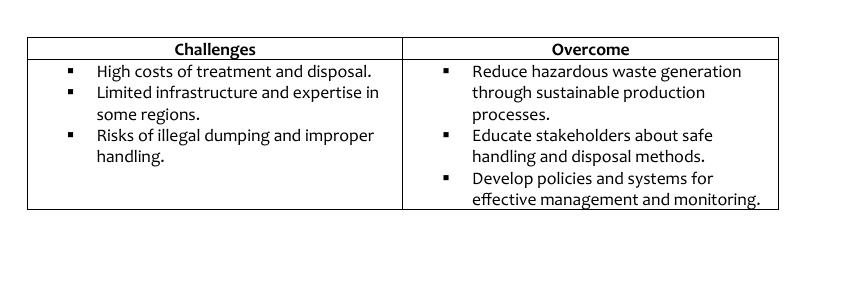
Biomedical waste management
Biomedical Waste Management (BMW) involves the proper handling, treatment, and disposal of waste generated by healthcare facilities such as hospitals, clinics, laboratories, and research institutions. Biomedical waste can pose risks to human health and the environment if not managed effectively.
➢ Categories of Biomedical Waste
Biomedical waste is classified into the following categories:

Steps in Biomedical Waste Management
1. Segregation- Waste is separated at the source into color coded containers or bags. As per colour codes.
2. Collection and Storage- stored temporarily in a secure area. Away from patient areas and comply with regulatory guidelines.
3. Transportation- Waste is transported in leak proof, labeled vehicles to treatment facilities.
4.Treatment Methods Autoclaving, Incineration, Microwave Treatment, Chemical Disinfection, Shredding.
5. Disposal- Treated waste is disposed of in authorized landfills or through deep burial for certain categories.
Environmental Impact Assessment and Environmental Management System – Introduction and its impact
➢ Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA)
Introduction: EIA is a systematic process used to identify, predict, and evaluate the potential environmental impacts of proposed projects or policies before they are implemented. It ensures that decision-makers consider environmental consequences along with economic and social factors.
Objective: To minimize negative environmental impacts and enhance positive outcomes.
Legal Framework: Many countries have regulations mandating EIA for specific projects (e.g., large infrastructure, industrial plants).
Impact of EIA:
1. Environmental Benefits: Prevents or minimizes environmental degradation.
2. Informed Decision-Making: Encourages sustainable practices in project design.
3. Social and Economic Gains: Balances development with community well-being.
4. Compliance Assurance: Helps projects adhere to environmental regulations.
➢ Environmental Management System (EMS)
Introduction: EMS is a framework that organizations use to systematically manage their environmental responsibilities. It helps them minimize negative impacts, comply with regulations, and improve overall environmental performance.
Objective: Achieve continual environmental improvement.
Standards: Often aligned with ISO 14001, an internationally recognized standard for EMS.
Impact of EMS:
1. Environmental Benefits: Reduces waste, pollution, and resource consumption.
2. Regulatory Compliance: Ensures adherence to environmental laws.
3. Cost Savings: Promotes efficient resource use and waste reduction.
4. Reputation Building: Demonstrates commitment to sustainability to stakeholders.
5. Risk Management: Minimizes risks associated with environmental liabilities.
➢ Combined Impact of EIA and EMS
When used together, EIA and EMS complement each other by integrating environmental considerations into the entire lifecycle of a project or operation.
- – EIA ensures sustainable project planning, while EMS ensures ongoing environmental performance during operations.
- – Together, they promote long-term environmental protection, regulatory compliance, and sustainable
development practices.

