UNIT 01: Introduction to presentation skills
Meaning of Presentation
A presentation is a method of communication in which an individual shares information with an audience to inform, persuade, or entertain. It often involves a combination of speech, visual aids (like slides), body language, and other tools.
Types of Presentations
a) Presentation that Deeply Involves the Audience
- Interactive in nature.
- Encourages audience participation through questions, discussions, activities.
- Often used in workshops, training sessions.
Benefits: Increases engagement, enhances understanding and retention.
b) Presentation that Creates Excitement
- Aims to inspire enthusiasm and interest.
- Often used for product launches, motivational talks.
- Uses dynamic visuals, energetic delivery, impactful stories.
- Focuses on tone, speed, and body language to maintain energy.
c) Persuasive Presentation
- Goal is to convince the audience to adopt a viewpoint or take action.
- Common in marketing, sales pitches, campaigns.
- Involves logic, emotion, and credibility (Ethos, Pathos, Logos).
- Includes clear call to action.
d) Presentation Evoking Emotional Appeal
- Uses stories, images, music, or real-life experiences to touch emotions.
- Often used in charity appeals, social cause awareness, motivational speeches.
- Helps audience connect personally with the message.
e) Presentation that Sells a New Idea
- Focuses on innovation or introducing a new concept/product.
- Emphasizes benefits, uniqueness, and relevance.
- Must address potential objections, use evidence to support claims.
Example: Startup pitches to investors.
f) Humorous Presentation
- Uses wit, jokes, or anecdotes to entertain or make content more relatable.
- Requires good timing, appropriateness, and audience understanding.
- Used in light-hearted speeches, after-dinner talks, or informal settings.
Planned and Unplanned Presentations
Planned Presentation
- Well-prepared, structured in advance.
- Includes defined objectives, organized content, and visual aids.
- Delivered in formal settings like conferences, meetings.
- Requires practice and rehearsal.
Unplanned Presentation
- Spontaneous or impromptu.
- Requires strong thinking on feet, confidence, and clarity.
- Example: Answering a sudden question in a meeting or giving a toast.
- May lacks structure but should still be coherent and engaging.
Planning a Presentation
Planning is essential to make a presentation effective, impactful, and audience-centric.
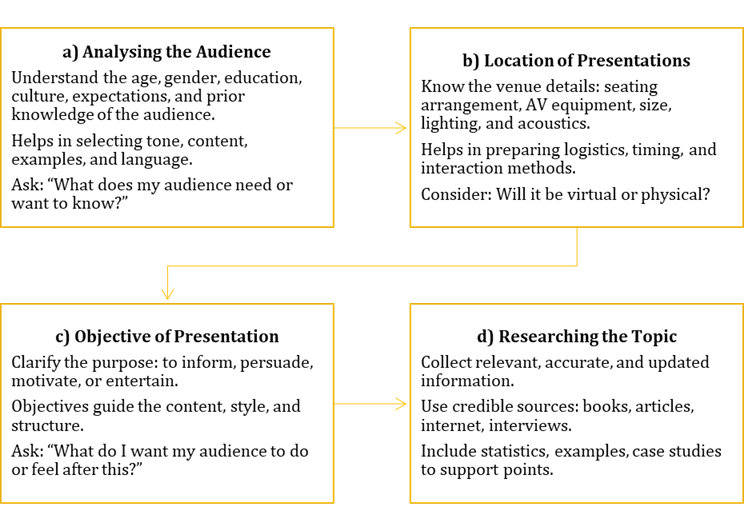
Structuring the Presentation
A well-structured presentation has three parts:
a) Introduction
- Grab attention: quote, story, question, or interesting fact.
- Introduce yourself and the topic.
- Give an overview of what will be covered.
b) Body
- Main content: organized into logical sections or points.
- Use headings, subheadings, and transitions.
- Support with data, visuals, anecdotes, and evidence.
c) Conclusion
- Summarize the key points.
- Reinforce the message or call to action.
- End with a strong closing: quote, challenge, or question.
Presentation Notes and Session Plan
a) Presentation Notes
- Speaker notes that help the presenter remember key points.
- Can include statistics, transitions, reminders for tone or body language.
- Avoid reading slides – notes should complement, not repeat, slide content.
b) Session Plan
- A blueprint of the entire session.
- Includes:
- Time allotment for each section.
- Activities or Q&A sessions.
- Breaks, interaction points.
- Helps in managing time and maintaining flow.



